Agentic Workflows: The Shift from Automation to Autonomy
Here's a sobering reality: The average knowledge worker burns 60% of their time on coordination instead of actual work hunting for information, waiting for approvals, chasing updates. That's 24 hours every week lost to operational friction.
As technologist Cal Newport put it: "The workflow that creates the shallow work often creates more shallow work."
Agentic workflows are changing that equation entirely.
Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid scripts, these AI-powered systems think, adapt, and handle complex processes independently. Companies implementing agentic AI are seeing 30-50% productivity improvements while slashing operational costs.
We're not talking about chatbots or RPA tools. Agentic workflows represent something fundamentally different systems that understand goals, reason through problems, make contextual decisions, and orchestrate actions across your entire tech stack without constant supervision.
Traditional automation asks: "Can I script this exact sequence?"
Agentic workflows ask: "What's the outcome we want?"—then figure out how to get there.
This isn't the future. It's happening now. And if you're still thinking about automation in flowcharts and if-then statements, you're already behind.
Let's explore what agentic workflows actually are, how they work, and how to implement them in your organization starting today.
What Makes A Workflow Agentic?
An agentic workflow is an AI-driven process that executes tasks dynamically with minimal human involvement to reach a specific goal. In simple terms, it's automation that can actually think.
These workflows run on agentic AI systems AI models with memory, planning, reasoning, and the ability to use tools. But here's what makes them truly different:
Traditional automated workflows are rigid. They follow fixed paths, and when something unexpected happens, they break. You've seen it: an approval gets stuck, a data field is missing, the whole process stops.
Agentic workflows are dynamic. They handle unexpected variables and tackle complex tasks that go way beyond what a simple script can do. Instead of blindly following steps, they constantly evaluate what to do next based on real-time information.
At their core, agentic workflows operate through a simple Thought–Action–Observation loop:
The AI assesses the situation → creates or updates a plan → takes action (using external tools or APIs) → observes what happened → repeats until the goal is met.
Here's a useful distinction: An AI agent is like a smart worker.
An agentic workflow is like an entire assembly line—coordinating AI systems, agents, humans, and distributed services into a structured, purposeful process.
How Workflows Evolved: Agentic vs AI vs Automated
Workflows themselves aren't a new concept.
At their core, they're coordinated sequences of tasks, managed by an orchestration layer, that work together to accomplish a specific goal. But there's a lot of confusion out there about what separates an agentic workflow from an AI workflow or a traditional automated workflow.
The real distinction comes down to how much AI autonomy is involved in reaching that goal.
Let's break it down with an example.
A traditional automated workflow relies on multiple pre-determined algorithmic scripts. Think of a customer service bot that follows a rigid set of steps or questions it can only help with issues that have been specifically coded in advance. If you ask it something outside its programmed responses, it hits a wall.
Now, agentic workflows are actually a subset of AI workflows. Non-agentic AI workflows use AI models to complete pre-determined workflow tasks. Picture an AI-powered expense approval flow or a RAG-based AI chatbot. These workflows definitely use AI, but the AI models aren't making autonomous decisions they're following a set path.
Agentic AI workflows are different. They include tasks that aren't predetermined, where AI models reason through situations and make their own decisions. For instance, imagine an expense approval flow where AI first determines whether an uploaded document is actually an expense, then decides whether to approve it for processing or send it to a human for review. Here, AI takes charge at critical decision points, making the workflow far more dynamic and powerful.
Automated vs AI-Powered vs Agentic Workflows
Area | Automated Workflows | AI-Powered Workflows | Agentic Workflows |
|---|---|---|---|
Workflow Logic | Fully pre-defined steps. | Pre-defined steps with some AI assistance. | High-level plan defined; specific actions decided dynamically. |
Task Execution | Logic- or rule-based tasks only. | AI handles complex tasks like classification or summarization. | AI performs most tasks, including reasoning, planning, and multi-step decisions. |
AI Involvement | None. | AI executes human-defined tasks. | AI makes decisions and executes tasks at runtime. |
Responsivity | Not adaptive to change. | Limited adaptability; can handle broader tasks. | Highly adaptive; responds to context and unexpected situations. |
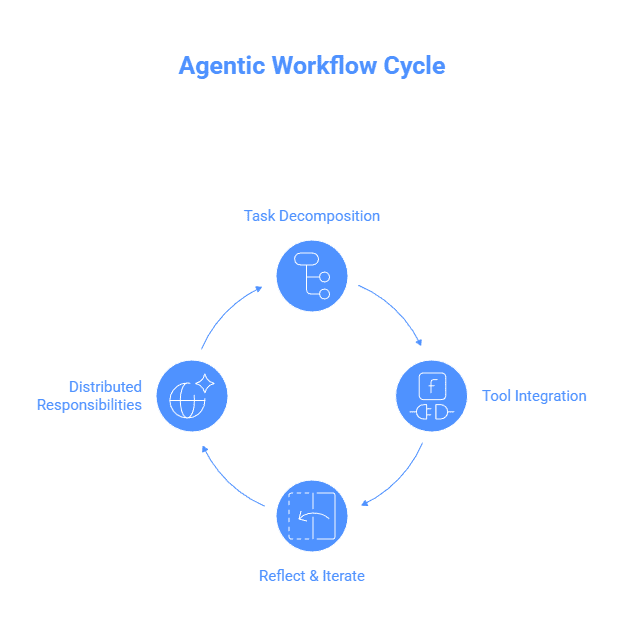
The Four Core Capabilities Of Agentic Workflows
For an AI workflow to be truly agentic, it needs these four capabilities:
1. Task Decomposition and Planning
Agentic workflows start by breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable components. When faced with a challenging goal, the system:
- Analyses the overall objective
- Identifies logical subtasks
- Maps dependencies between steps
- Creates a sequential priority list
Take processing insurance claims, for example. An agentic system doesn't just follow a checklist it identifies what's actually needed: validating customer information, reviewing policy details, checking for fraud indicators, calculating payouts. Then it creates an execution plan that accounts for how these steps depend on each other.
2. Tool Use and Integration
At execution time, agentic workflows pull data from multiple sources—sensors, databases, APIs and decide what to do next.
This concept started with computer vision challenges. Early language models couldn't process images, so developers created functions linking them to visual APIs. As models like GPT evolved, this approach exploded.
Modern agentic workflows connect with external resources like:
- Web search engines for current information
- Code interpreters for running computations
- APIs for interacting with other services
- Data stores for retrieving specialized knowledge
The selection of tools can be predetermined or left to the agent's discretion. For complex tasks, letting the agent choose works best. Simpler workflows benefit from predefined tool selection.
3.Reflect and Iterate
Here's where it gets interesting: the job isn't done after task execution. Agentic workflows improve through self-evaluation. Rather than delivering single-attempt outputs, they review their work, spot problems, and make refinements.
The workflows store context and feedback across interactions through memory capability in two forms:
Short-term memory tracks recent conversation history and current task progress, helping the agent maintain context and determine next steps.
Long-term memory stores information across multiple sessions, enabling personalization and performance improvements over time.
Without memory, AI systems would restart from scratch with each interaction. Memory transforms one-off interactions into ongoing, evolving relationships.
4. Distribute Responsibilities
Complex tasks often require multiple types of expertise. Agentic workflows distribute work across specialized AI agents each handling different aspects, much like human teams collaborate on complex projects.
Picture customer service automation with multi-agent collaboration:
- One agent interprets customer requests
- Another searches knowledge bases for relevant information
- A third crafts personalized responses
- A supervisor agent coordinates the entire process
This division of labour enhances overall performance by leveraging each agent's strengths. It's particularly effective for tasks requiring diverse skills or parallel processing the kind of work that would normally require an entire team.
Top 3 Agentic Workflow Examples
1. Finance: Invoice Processing
Typical workflow: Finance Invoices arrive in the AP inbox and get captured by automation tools, but someone still needs to verify them manually. AP analysts switch back and forth between invoicing and contract systems to check terms, spend time resolving discrepancies through emails and calls, and eventually request approval. Even after approval comes through, payment steps often require manual data entry and system updates.
Agentic workflow: An intake agent validates incoming invoices and creates payment requests. A contract agent cross-references contract terms and handles vendor communication automatically to resolve any discrepancies. An approval agent looks at historical patterns and recommends approval before routing to the appropriate owner. A payment agent processes the payment and updates all relevant financial systems.
This approach cuts down on errors, accelerates processing time, and strengthens compliance.
2. IT: Network Threat Detection
Typical workflow: Monitoring tools gather traffic logs and threat intelligence, then analysts dig through anomalies, validate alerts, correlate data points, and determine how severe an incident is. Once they confirm a threat, they manually execute containment measures and document everything for compliance purposes.
Agentic workflow: A monitoring agent constantly analyzes network data and threat feeds. When it spots a risk, a threat response agent automatically validates the threat, applies containment procedures, and documents each action taken. An optimization agent reviews the response, updates security rules, and fine-tunes the overall security posture.
This creates a continuous, autonomous threat detection system with immediate response capabilities.
3. Healthcare: Prior Authorization
Typical workflow : Providers submit authorization requests manually, and staff members review medical documentation, check insurance guidelines, and communicate back and forth with payers. Delays pile up because of missing documents, repeated outreach attempts, and manual evaluation steps.
Agentic workflow for health care: An intake agent collects clinical documents, validates completeness, and checks eligibility against guidelines. A review agent analyzes clinical information against payer rules and flags any missing details. A communication agent manages interactions with providers and payers to get clarifications or additional documents. Once authorization is approved, the agent updates EMR systems and notifies both the patient and provider.
This transforms prior authorization from a sluggish, manual process into an intelligent, proactive workflow.
The Components Of Agentic Workflow
Agentic workflows are built on afoundation of Intelligent Automation, which helps businesses create secure, AI-powered automated processes with proper oversight. The main building blocks RPA, NLP, AI agents, workflow orchestration, and integrations—all work together to create dynamic, automated processes that adapt and respond intelligently.
Agentic workflows combine intelligent automation, AI agents, and orchestration to execute adaptive, end-to-end processes with oversight and reliability.
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA handles repetitive, rule-based tasks like data entry or transaction processing. In agentic workflows, RPA executes precise actions—for example, taking AI-extracted invoice data and entering it into an accounting system automatically.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP lets agents understand and respond to human language, enabling natural interactions. It powers chatbots, sentiment analysis, and content generation, making agent communication intuitive and context-aware.
3. AI Agents
AI agents perform complex reasoning, planning, and decision-making using LLMs. They use function calling to execute actions, access tools, query systems, and collaborate with automation layers to complete real tasks reliably.
4. Workflow Orchestration
Orchestration coordinates the full process—setting task order, handling dependencies, routing outputs, and managing timing. Tools provide visual maps that simplify managing multi-system, multi-step workflows.
5. Integrations & APIs
Integrations link all systems (CRMs, databases, apps) so agents and automations can share data and act seamlessly. They ensure the whole workflow operates as a unified, connected process.
Steps for Implementing AI Agentic Workflows
Implementing agentic workflows isn't just about adding AI it's about rethinking how your business operates. Here's a practical approach to building workflows that deliver measurable results.
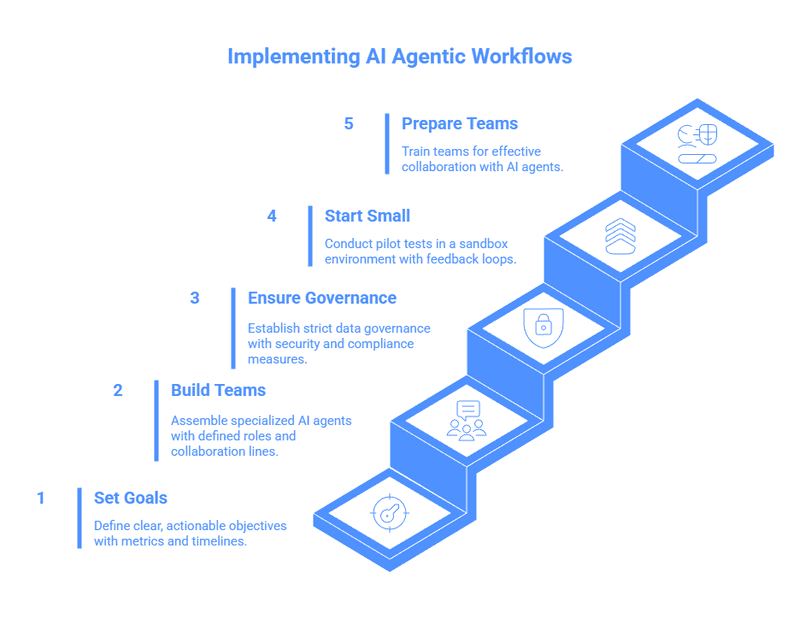
Step 1: Set Specific, Actionable Goals
Get your entire organization aligned on why you're adopting agentic workflows. Assess your infrastructure, budget, and technical capabilities.
Agentic AI needs clarity. Vague goals like "improve efficiency" won't cut it. Your objectives must be specific, time-bound, and measurable.
Examples:
- Cut customer service response time from 10 minutes to 2 minutes
- Boost first-contact resolution by 25%
- Reduce compliance review times by 40%
Clear goals give each agent direction and help the workflow optimize toward real outcomes.
Step 2: Build Teams of Specialized AI Agents
Think role-based micro agents, not one "super agent." Each specialist should:
- Connect to specific systems
- Handle focused tasks
- Collaborate and hand off work autonomously
Break your workflow into stages and assign the right agent to each—just like building a real team.
Step 3: Ensure Strict Data Governance
Strong governance is non-negotiable:
- Track every data movement with metadata and audit trails
- Define clear access permissions and usage rules
- Run regular audits for accuracy and compliance
- Update policies as regulations evolve
Security essentials:
- Use encryption and secure APIs
- Follow GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS requirements
- Document decision-making processes
- Be transparent about data collection and usage
Step 4: Start Small with Test Runs
Launch a small, high-impact pilot with clear boundaries, quick feedback loops, and clean data. This helps you identify integration gaps, data quality issues, and realistic ROI before scaling across the organization.
Step 5: Prepare Your Team for AI Collaboration
Train employees on:
- Effective prompting techniques
- When to trust vs. verify agent decisions
- Human-agent handoff points
- Supervising escalations and exceptions
This transforms AI from a threat into a productivity partner.
When to Use an Agentic Workflow
Use an Agentic Workflow when you need a structured, reliable, multi-step process that involves multiple AI components working together with clear checkpoints and high accuracy.
Factor | What It Means | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Task Complexity | Ideal for complex, multi-stage tasks that must be broken into coordinated sub-tasks. | Automated report creation with multiple agents researching, analyzing, drafting, and publishing. |
Control & Governance | Best when you need predictable structure, validation steps, and human oversight. | Invoice processing with PO matching, human review, and automated payment scheduling. |
Output Type | Suited for fully autonomous, end-to-end business processes. | Client onboarding with document checks, verifications, and system updates. |
Development Needs | Works for production systems requiring reliability, scalability, and easy debugging. | Supply-chain automation using real-time logistics and inventory data. |
Benefits and Challenges of agentic workflows
Benefits Of Agentic Workflows
- Increased Efficiency Agentic workflows automate complex, repetitive tasks at high speed—cutting bottlenecks and completing processes like invoice handling far faster than manual teams.
- Enhanced Decision-Making AI agents analyze real-time data, detect patterns, and make routine decisions autonomously—such as isolating cyber threats instantly to reduce response delays.
- Improved Accuracy They execute tasks with consistent precision, catching and correcting errors immediately, improving data quality and reducing human mistakes.
- Scalability Agentic systems easily handle high volumes of work, intelligently distributing tasks—ideal for managing spikes in orders, support, or operations.
Challenges of Agentic Workflows
- Technical Overhead Agentic workflows require heavy setup, infrastructure, and engineering effort. For simple processes, the complexity may outweigh the value unless the right tools and frameworks streamline development.
- Risk of Unreliability Because agentic systems can behave unpredictably, they may make incorrect or harmful decisions. Strong guardrails, human oversight, and rigorous testing are essential to keep them safe and reliable.
Top Agentic Workflow Orchestration Frameworks
These are the open-source libraries that provide the core logic and building blocks for creating complex, multi-step agent systems.
Framework | What It Does | Best For |
|---|---|---|
LangGraph | Graph-based state management with loops, branches, and checkpoints. | Complex, stateful, production workflows with human review. |
Microsoft AutoGen | Multi-agent conversations that debug, reason, and solve problems together. | Autonomous teamwork, coding tasks, problem-solving agents. |
CrewAI | Role-based agents working in sequence or hierarchy. | Structured collaboration—researcher, writer, editor workflows. |
LangChain | Core toolkit for LLMs with massive tool integrations. | Single-agent flows and plugging into any API/data source. |
Best Practices For Building Agentic Workflows In 2026
1. Architecture & Design
Use a Two-Tier Agent Model
- Orchestrator Agent: Manages goals, breaks down tasks, and coordinates the workflow.
- Worker Subagents: Simple, stateless units that handle one narrow, testable function.
- This keeps behavior predictable and debugging easy.
Adopt Graph-Based Orchestration
- Use LangGraph or similar tools to visualize states, loops, branches, and handoffs.
- Enables deterministic flows, safer decisions, and clearer recovery paths.
Design Tool-First Actions
- Maintain a governed tool registry with rate limits and access control.
- Use ReAct-style steps (Thought → Action → Observation) to keep agents grounded in real data.
2. Governance & Reliability
Include Human-in-the-Loop (HIL)
- Add escalation points for sensitive tasks (refunds, compliance, security signals).
- Provide full context—reasoning, tools used, and plan—so humans can act fast.
Make Every Step Auditable
- Log prompts, tool calls, subagent outputs, reasoning, and final decisions.
- Use structured schemas to validate outputs and enforce business rules.
Handle Failure Safely
- Implement fallback flows: retries, downgraded tools/models, or human escalation.
- Track workflow metrics (success rate, latency, cost) to improve reliability.
3. Optimization & Cost Efficiency
Match Model Size to Task
- Use top-tier models for planning and complex reasoning.
- Use smaller, fast models for extraction, tagging, or routine checks.
Cache Repeated Prompts
Cache common LLM calls to reduce cost and boost speed.
Compress Context with RAG
- Retrieve only the most relevant snippets instead of dumping full knowledge bases.
- Leads to cheaper, faster, and more accurate agent decisions.