The Landscape of AI Agents: Finding the Right Platform for Agentic Execution
Over the last two years, the market for AI agents has exploded. Every vendor, from startups to enterprise software giants, now claims to offer the next breakthrough in autonomous systems. Yet beneath the noise lies a fundamental truth: most of what is marketed as AI agents today are not truly agentic. They are task bots wearing a futuristic label, rigid systems wrapped in conversational interfaces, or simple automations upgraded with an LLM.
A real AI agent platform does something else entirely. It orchestrates intelligence across data, actions, tools, and evolving customer intent. It becomes an adaptive decision layer, dynamic, contextual, and memory-driven.
And as organizations move from rule-based journeys to autonomous customer engagement, the gaps between simple AI agent frameworks and orchestration-grade platforms grow painfully visible.
There’s a vast difference between an AI that responds and an AI that reasons. One reacts. The other orchestrates.
This blog explores that divide, mapping the landscape of emerging platforms, examining what true agentic execution requires, and highlighting why the future belongs to systems that unify intelligence across your existing stack not tools that operate in isolation.
Beyond Frameworks: Differentiating True Agentic AI Platforms from Simple Tools
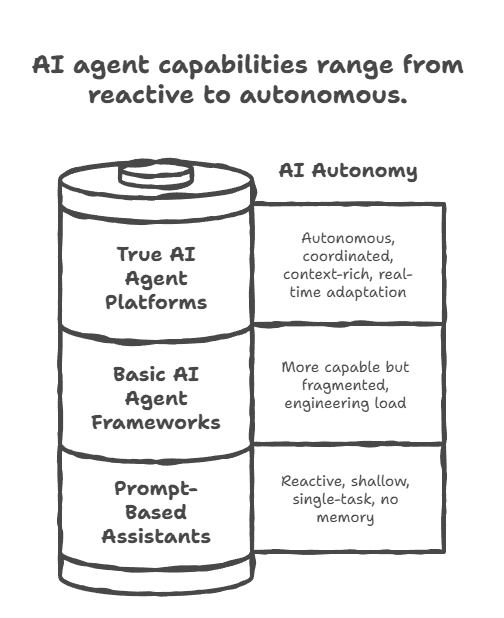
Most products marketed as "AI agents" today fall into three distinct categories, and understanding the difference determines whether you build autonomous systems or just add another tool to your stack.
Prompt-Based Assistants: The Illusion of Intelligence
These are single-task, reactive bots that operate in isolation:
- No persistent memory across interactions: Every conversation starts from zero, forcing customers to repeat information and context they've already shared.
- Limited to predefined responses: They follow rigid scripts without understanding intent or adapting to unexpected scenarios.
- Great for content generation, terrible for orchestration: They can draft emails or summarize documents, but can't coordinate multi-step workflows across your systems.
Basic AI Agent Frameworks: Better Execution, Still Siloed
AI agent frameworks and even the best AI agent framework options provide routing, tool-use, and planning basics, but they share critical limitations:
- Require heavy engineering investment: Your technical teams spend months building custom logic, integrations, and maintenance protocols instead of focusing on strategy.
- Operate in information silos: They can't access unified customer data, so they make decisions based on incomplete context.
- Improve individual tasks without unifying the stack: Each framework handles specific functions well, but doesn't coordinate intelligence across your marketing, sales, and support systems.
True AI Agent Platforms: Orchestration at Scale
A genuine AI agent platform orchestrates data, tools, channels, and tasks into cohesive autonomous systems:
- Enable autonomous, multi-step workflows: The platform handles complex sequences—qualifying leads, routing conversations, updating records, triggering campaigns without requiring human intervention at each step.
- Maintain context and memory across channels: Customers can start conversations via chat, continue through email, and complete actions in-app while the system retains full context.
- Adapt decisions in real time based on outcomes: Rather than following predetermined paths, the platform evaluates results and adjusts strategy dynamically.
- Support cross-stack intelligence: The system ingests signals from CRM, marketing automation, support platforms, and analytics tools to build complete customer understanding.
Bottom line: Agentic execution requires orchestration, not single-function automation. Most legacy frameworks aren't built for that future.
The Data Foundation: Eliminating Silos to Build the Marketing Memory Bank
No agent can act autonomously without a unified data layer. Period. Your AI is only as intelligent as the information it can access, and fragmented data creates fragmented experiences.
What a Real Marketing Memory Bank Must Include
True ai agents software depends on comprehensive, continuously updated data:
- Cross-channel behaviors from every touchpoint: Website visits, app interactions, CRM records, LMS engagement, support tickets, and email responses all feed into one unified profile.
- Qualitative signals beyond demographics: The system captures sentiment from conversation analysis, urgency from interaction timing, intent from behavior patterns, and friction points from dropout moments.
- Historical interactions and preferences: Past conversations, purchase patterns, content engagement, and stated preferences inform every future interaction.
- Real-time updates based on current actions: When customers browse pricing pages, abandon carts, or engage with specific content, the data layer updates immediately and triggers appropriate responses.
Why This Foundation Matters for Autonomous Operation
Without unified data, your agents can't deliver ai personalization marketing that actually feels personalized:
- Personalize at scale without manual segmentation: The system dynamically groups customers based on behavior, intent, and context rather than relying on static demographic segments.
- Predict intent before customers explicitly state it: By analyzing conversation patterns and engagement signals, the platform identifies buying readiness and optimal timing for outreach.
- Trigger autonomous journeys that adapt to behavior: When customers deviate from expected paths, the system adjusts strategy rather than continuing with irrelevant scheduled touchpoints.
- Maintain state across long-running tasks: For complex sales cycles or extended onboarding sequences, the platform preserves context across weeks or months of interactions.
The distinction between marketing orchestration platform capabilities and basic automation starts here. If your data lives in silos, your agents will operate in silos no matter how sophisticated the AI model underneath.
Comparing Leading Platforms for Agentic Execution
The ai agent platform market segments into three distinct categories, each with different architectural philosophies and use case alignment. Understanding these categories helps organizations identify the best ai agent framework for their specific requirements.
Developer-Centric Frameworks: Maximum Flexibility, Maximum Complexity
Ai agent frameworks provide low-level primitives that technical teams assemble into custom solutions:
Granular control over every component: Developers select specific memory stores, choose reasoning algorithms, configure tool integrations, and design orchestration logic tailored to unique requirements that off-the-shelf solutions cannot accommodate.
Complete architectural freedom: Organizations can implement novel approaches, experiment with cutting-edge techniques, and optimize every aspect of agent behaviour without vendor-imposed constraints or limitations.
Significant engineering investment required: This approach demands strong technical teams, extended development timelines, and ongoing maintenance overhead as frameworks evolve and business requirements change.
Organizations with sophisticated engineering resources and truly unique requirements benefit from this approach, but the implementation complexity makes it unsuitable for most marketing and revenue operations teams seeking rapid deployment.
Vertical-Specific Solutions: Rapid Deployment, Limited Adaptability
Vertical solutions target particular industries or functions with pre-configured agents and workflows:
Industry-specific templates and configurations: Customer service platforms include support ticket routing, knowledge base integration, and escalation logic configured for common scenarios, enabling deployment in weeks rather than months.
Pre-built integrations with category-standard tools: These agentic ai tools connect seamlessly with popular platforms within their vertical, reducing integration effort and accelerating time-to-value for organizations using standard technology stacks.
Rigid assumptions that constrain customization: Organizations frequently discover that the assumptions baked into vertical solutions conflict with their unique processes, brand voice, or strategic differentiation, leading to workarounds that undermine efficiency gains.
Orchestration Layers: Vendor-Agnostic Intelligence Hubs
Marketing orchestration platforms represent the emerging category that addresses limitations of both frameworks and vertical solutions:
Intelligence layer that enhances existing systems: Rather than replacing CRM, marketing automation, or engagement tools, these platforms act as a coordination brain that makes disconnected systems operate as unified intelligence.
Vendor-agnostic integration across the martech stack: The platform ingests data from existing tools, applies sophisticated reasoning, and triggers actions through current systems, preserving technology investments while eliminating silos that create fragmented customer experiences.
Strategic flexibility without technical complexity: Marketing and revenue operations teams gain AI-powered capabilities without building custom code, migrating data, or abandoning established processes that teams understand and trust.

Evaluating Architecture: Single vs Multi-Agent Systems
The architectural decision between single-agent and multi-agent systems profoundly impacts scalability, maintainability, and operational complexity.
Single-Agent Architectures: Simplicity with Scaling Limitations
Single-agent systems centralize all logic within one coordinated system:
Simplified deployment and reduced coordination overhead: With one agent handling all interactions and decisions, organizations avoid the complexity of inter-agent communication protocols, conflict resolution mechanisms, and distributed state management.
Clear accountability for outcomes: When something succeeds or fails, identifying root causes becomes straightforward because all logic resides in one place rather than being distributed across multiple specialized components.
Limited specialization and scaling constraints: As requirements grow more sophisticated, single agents become increasingly complex, making updates risky and feature additions difficult without unintended consequences affecting unrelated functionality.
Multi-Agent Systems: Specialized Capabilities Through Coordination
Multi-agent architectures distribute responsibility across specialized agents that collaborate toward shared objectives:
Functional specialization with clear boundaries: One agent focuses on conversation analysis, while another handles workflow execution and a third manages compliance checks, enabling deep expertise in each domain without forcing compromise across competing priorities.
Independent scaling of specific capabilities: Organizations can enhance conversation analysis without modifying workflow logic, or add new compliance rules without touching customer engagement systems, reducing deployment risk and accelerating iteration.
Coordination complexity requiring robust orchestration: The Cross-Stack Journey Orchestration Architecture Patterns must implement governance mechanisms preventing agents from conflicting actions while ensuring effective collaboration, demanding sophisticated orchestration frameworks.
Leading agentic ai vendors increasingly adopt hybrid approaches combining central orchestration with specialized agent capabilities, providing coordination clarity with functional specialization benefits.
Integrating Agentic AI with Enterprise Workflows
Technical capability means nothing without seamless integration into existing enterprise workflows. The most sophisticated ai agent platform fails if it cannot connect with systems powering daily operations.
Data Integration: Building Complete Customer Context
Platforms must connect across three critical layers:
CRM and marketing automation for behavioral data: Integration with Salesforce, HubSpot, Marketo, and similar platforms provides transaction history, campaign engagement, and opportunity stage information that contextualizes every customer interaction.
Support and engagement systems for interaction history: Connections to Zendesk, Intercom, and communication platforms capture the complete conversation timeline, ensuring agents never ask customers to repeat previously shared information.
Analytics and business intelligence for strategic context: Integration with data warehouses and BI tools enables agents to consider market trends, competitive dynamics, and business performance when making decisions about resource allocation and strategic priorities.
Action Execution: Triggering Workflows Across Systems
Integration enables autonomous operation rather than advisory recommendations:
CRM automation for opportunity and task management: When agents identify high-intent prospects, they create opportunities, assign ownership, set follow-up tasks, and update pipeline forecasts without requiring manual data entry from sales teams.
Marketing automation for campaign enrolment: The system dynamically enrols contacts in nurture sequences, adjusts email cadences based on engagement, and personalizes content recommendations through existing marketing platforms rather than requiring parallel campaign management.
Communication orchestration for true omnichannel delivery: Agents trigger emails, SMS, push notifications, and in-app messages through established systems, ensuring consistent brand voice and respecting communication preferences while delivering omnichannel communications that feel coordinated rather than random.
Governance Integration: Operating Within Compliance Frameworks
Enterprise organizations maintain elaborate approval workflows and audit requirements:
Compliance rule engines for regulatory adherence: The platform checks all customer communications against GDPR, CCPA, TCPA, and industry-specific regulations before execution, automatically suppressing actions that would violate consent or create legal exposure.
Approval workflows for high-stakes decisions: Significant actions like pricing adjustments, contract terms, or executive escalations route through existing approval chains rather than bypassing established governance to move faster.
Audit trails for accountability and learning: Every agent decision, data access, and action execution generates comprehensive logs that satisfy compliance requirements while enabling continuous improvement through outcome analysis.
Building a Scalable Future for Agentic Intelligence
Scalability encompasses technical performance, operational complexity, and strategic adaptability that determine whether initial pilots expand into enterprise-wide transformation.
Technical Scalability: Performance Under Growing Demand
Platforms must handle increasing interaction volumes without degradation:
Horizontal scaling for conversation and analysis workloads: As organizations deploy agents across more channels and customer segments, the infrastructure must add capacity seamlessly while maintaining response quality and consistency.
Efficient resource utilization for cost management: The system should optimize compute usage through intelligent caching, parallel processing, and selective model invocation, preventing costs from scaling linearly with usage.
Sub-second response times even at scale: Customers expect immediate responses regardless of backend complexity, requiring architectures that minimize latency through distributed processing and predictive pre-computation.
Operational Scalability: Managing Complexity Without Proportional Headcount
The ROI performance efficiency depends on whether small teams can oversee sophisticated implementations:
Intuitive monitoring and observability: Teams need clear visibility into agent decisions, interaction outcomes, and system health without requiring data science expertise to interpret complex metrics or troubleshoot issues.
Configuration-driven customization: Adjusting agent behavior, updating business rules, and refining orchestration logic should happen through visual interfaces rather than requiring code changes and engineering deployments.
Self-service troubleshooting and optimization: When performance degrades or outcomes disappoint, teams should access diagnostic tools, performance benchmarks, and optimization recommendations that enable improvement without vendor dependency.
Strategic Scalability: Adapting to Evolving Business Requirements
Markets shift, products change, and customer expectations evolve continuously:
Incremental enhancement without re-architecture: Organizations should add new capabilities, integrate additional systems, and expand to new channels through configuration and integration rather than fundamental rebuilding of agent logic.
Learning and improvement mechanisms: The platform must capture outcomes, analyze what works, and automatically refine strategies over time, becoming more effective as it processes more interactions rather than requiring periodic manual tuning.
Clear Implementation Timeline from pilot to production: Agentic AI vendors should provide structured frameworks showing how organizations progress from initial use cases to comprehensive deployment, with realistic milestones and resource requirements at each stage.
The Final Check: Evaluating Agentic AI Vendors and Choosing the Right Stack
When reviewing agentic AI vendors and identifying the best AI agent framework, organizations must demand transparency and proof beyond marketing claims:
Verifiable Implementation Timeline with realistic milestones: Request detailed project plans showing how long integration takes, when value begins accruing, and what resources each phase requires, then validate against customer references rather than accepting vendor assertions.
Comprehensive Evaluation And RFP Kit for objective comparison: Demand standardized evaluation frameworks that enable apples-to-apples comparison across vendors, including technical architecture assessments, integration complexity analysis, and total cost of ownership modeling.
Proof of ROI performance efficiency through customer case studies: Look for detailed documentation of business outcomes, conversion rate improvements, cost reductions, efficiency gains with clear attribution to the platform rather than confounding factors like market conditions or concurrent initiatives.
The questions that matter involve architectural philosophy, integration depth, and strategic approach rather than feature lists and impressive demonstrations.
The Zigment Difference
This brings us to Zigment’s perspective on the future of agentic AI.
Most tools focus on tasks. Some focus on workflows. Very few focus on unifying the entire ecosystem. Zigment is built on a different philosophy: your systems shouldn’t be replaced; they should be harmonized.
Zigment acts as the agentic AI layer across the enterprise, integrating intelligence and execution across CRMs, marketing platforms, support systems, and data warehouses. Instead of building yet another destination tool, Zigment becomes the vendor-agnostic conductor, turning fragmented data and interactions into coordinated, autonomous journeys.
This approach solves the deepest industry problem: siloed intelligence.
With Zigment, organizations gain:
- A real-time Marketing Memory Bank
- Autonomous conversation and journey orchestration
- Workflow intelligence that adapts in milliseconds
- A unified cross-stack architecture
- Consistent omnichannel communications
- Full compliance, traceability, and governance
It is the intelligent orchestration layer that transforms your entire stack into a synchronized intelligent ecosystem.