Agentic Architecture: How the Intelligent Layer Powers AI
Most companies think they’re building AI agents. In reality, they’re assembling elaborate chatbots.
That distinction matters and it all comes down to architecture.
When people talk about agentic models, goal-oriented systems, or multi-agent intelligence, the conversation often jumps straight to LLMs. But large language models are only one piece of the puzzle.
The real breakthrough is the part that transforms reactive assistants into autonomous agents that can plan, coordinate, and act is the Agentic Architecture and the Intelligent Layer sitting beneath them.
This layer is the missing ingredient inside most enterprise stacks.
It unifies fragmented data sources, synchronizes structured CRM records with unstructured human signals, and gives autonomous agents the reasoning, lifecycle management, and real-time context required to operate in the real world. Without it, organizations end up with disconnected automations masquerading as intelligence.
Agentic AIarchitecture is not about deploying a clever model rather it’s about building the high-level structured and unstructured data agent, the capability knowledge graph, and the integration layer that allows agents to communicate, adapt, and execute across your entire ecosystem.
This is where traditional AI vs agentic AI architecture becomes a night-and-day difference!
You’re not just adding AI into your stack—you’re redesigning how your stack thinks.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to a sophisticated platform layer that uses real-time intelligence derived from conversations to execute and govern autonomous customer journeys and operational tasks. It is explicitly positioned as the unifying technology layer for the marketing stack.
Unlike traditional automation that waits for instructions, agentic systems reason about what to do next.
They process structured CRM data, unstructured human signals, real-time events, and capability knowledge graphs to decide on the best course of action. These systems feel more like collaborators than scripts. They analyse context, predict outcomes, and adjust strategy based on continuous learning.
Traditional AI vs. Agentic AI: Key Differences
Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|
1. Follows predefined rules and workflows | 1. Sets goals, plans tasks, and adapts autonomously |
2. Reactive to inputs | 2. Proactive in identifying opportunities and next actions |
3. Requires task-specific instructions | 3. Interprets intent and determines the best approach |
4. Limited to narrow tasks | 4. Capable of complex, multi-step reasoning |
5. Static behaviour unless reprogrammed | 5. Continuously learns from real-time feedback |
6. Works in isolated systems | 6. Operates across multi-agent environments |
7. Depends heavily on manual oversight | 7. Uses human oversight strategically, not operationally |
8. Optimized for accuracy of a single output | 8. Optimized for achieving outcomes and goals |
9. Processes only structured or labelled data well | 9. Understands structured and unstructured signals together |
10. Limited integration with external tools | 10. Executes actions across tools, APIs, and real-world systems |
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Agentic AI architectures stand out due to several interrelated features that enable agents to excel in challenging, constantly changing environments. These key characteristics distinguish them from other autonomous AI systems and traditional automation.
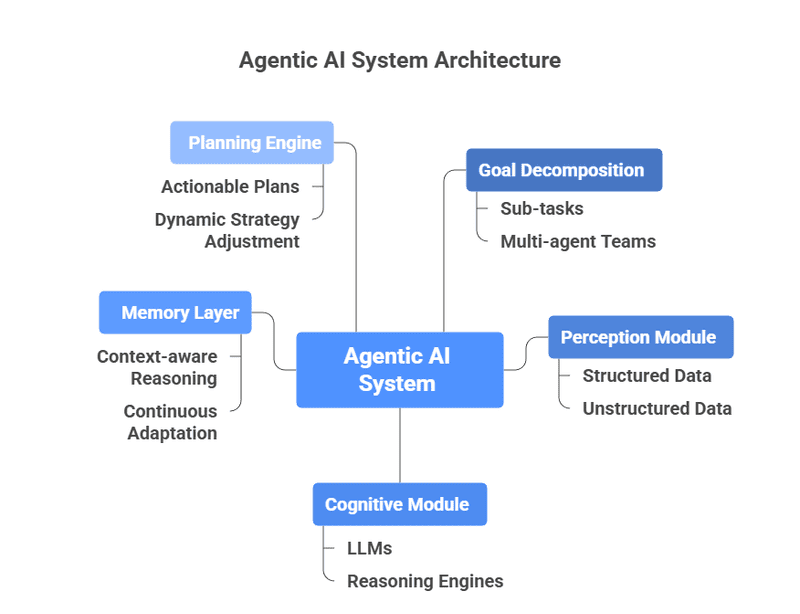
Continuous Learning - Agentic AI systems constantly refine their strategies using feedback loops, allowing them to learn from both outcomes and changing information in real time. This is achieved through techniques like reinforcement learning or meta-learning, ensuring agents adapt quickly and improve their task performance without manual retraining.
Goal Decomposition - Rather than tackling multi-step problems holistically, agentic agents break down large objectives into manageable sub-tasks, sequencing and distributing them as needed—often in multi-agent teams. This robust orchestration layer ensures complex tasks get executed efficiently and adaptively, as each agent can specialize and adjust as subtasks evolve.
Perception Module - This module functions as the agent’s sensory system, processing diverse data sources—ranging from structured databases and APIs to spoken commands, sensor streams, and visual input. Advanced agents combine techniques like computer vision and natural language processing to interpret high-level signals from both structured and unstructured data.
Cognitive (Reasoning) Module - Serving as the brain, this component integrates large language models (LLMs) or dedicated reasoning engines. It interprets inputs, defines objectives, reasons through possibilities, and formulates action plans—bridging perception and execution for advanced decision-making.
Memory Layer - Agents require persistent memory to store and recall context, past transactions, and historical data, enabling them to learn from experience and improve future decisions in real time. Memory underpins context-aware reasoning and continuous adaptation.
Planning Engine - This module is responsible for decomposing complex goals into actionable plans, stitching together sequences of tasks, and adjusting strategies dynamically as new data arrives. Advanced planning engines manage uncertainty and evolve strategies as conditions change.
Integration & Orchestration Layer - This intelligent layer coordinates multiple agents and components, managing data flows and workflow scheduling, and ensuring smooth integration with external enterprise systems or other agents. It handles collaboration, communication, and the overall cohesion required for multi-agent solutions.
Feedback Loop - After actions are executed, this post-action review process allows agents to learn, adapt strategies, and mitigate future errors. Continual feedback promotes improvement and resilience, ensuring agents aren’t stuck on outdated routines.
These layers come together to form robust agentic AI systems that operate autonomously, make reliable decisions, and evolve with changing contexts and continual feedback, setting them apart from traditional automation approaches.
Types of Agentic AI Architectures
Agentic AI systems are built on distinct architectural models tailored to fit various autonomy, collaboration, and scalability requirements. Below are the primary types of agentic AI architectures, with their structures and advantages explained.
Hierarchical Multi-Agent Architectures
Agents are organized in vertical tiers with clearly defined roles. Top-level (leader) agents set strategy and goals, making high-level decisions, while lower-level agents execute tasks, report back, and escalate issues as needed. This centralized structure supports accountability and sequential execution in workflows, making it suited for processes requiring structured leadership.
- Benefits: Clear accountability, well-defined communication, efficient management of complex tasks.
- Best fit: Workflows with strategic oversight, sequential task execution.
Horizontal (Peer-to-Peer) Architectures
All agents operate as equals on the same level, collaborating and coordinating actions without any structured hierarchy. Decisions are made collectively, supporting dynamic problem solving and parallel service execution. This decentralized system is best for situations demanding creativity, innovation, and flexibility.
- Benefits: Enhanced creativity, distributed knowledge, adaptable in fast-changing scenarios.
- Best fit: Collaborative design, brainstorming, tasks needing varied expertise.
Hybrid Architectures
This model merges hierarchical and peer-to-peer approaches, allowing agents to operate independently or escalate issues up the chain when complexity or authority oversight is necessary. Leadership and collaboration are dynamically assigned according to the needs of the task, creating versatility and balance between structure and flexibility.
- Benefits: Flexible leadership, scalable for complex and dynamic tasks, balances innovation and effectiveness.
- Best fit: Strategic planning, dynamic team projects, mixed workflows.
Enterprise-Wide Architectures
Centralized platforms, such as Zigment, connect agents throughout an organization, tying together autonomous teams via a central orchestration backbone. These systems manage distributed agents and integrate data sources, enabling seamless collaboration and oversight across enterprise operations.
- Benefits: Organization-wide management, scalable integration, holistic data and workflow coverage.
- Best fit: Large-scale operations, enterprise digital transformation, cross-departmental coordination.
Choosing the right architecture depends on your organization’s size, complexity, operational structure, and integration demands, ensuring agents collaborate and scale effectively across business use cases
Best Practices for Designing Agentic AI Architecture
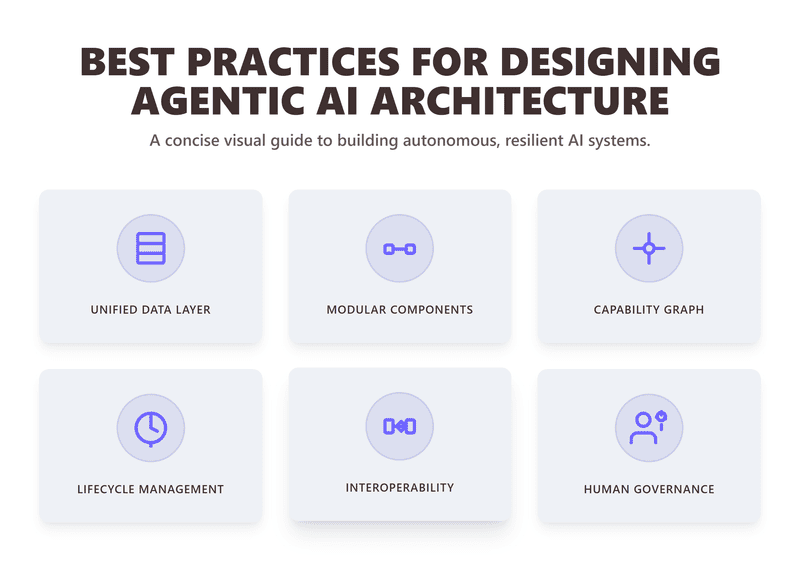
Building the right foundation unlocks true autonomy and resilience. Streamline your architecture with these principles:
- Start with a Unified Data Layer: Centralize high-fidelity data sources for both structured and unstructured input. This enables real-time, context-rich reasoning.
- Embrace Modular Components: Adopt a plug-and-play style—mixing different goal-oriented, high-level, and unstructured data agents as needed.
- Utilize a Capability Knowledge Graph: Store not just facts, but relationships and dependencies between agents, tasks, and data.
- Robust Lifecycle Management: Ensure agents can self-initiate, halt, or escalate tasks for adaptive, fail-safe operation.
- Build with Interoperability in Mind: Make it simple for agents to communicate with real-world systems be it databases, CRMs, or IoT sensors.
- Govern with Human Oversight Where Necessary: Keep critical exceptions, compliance, or sensitive decisions under human review.
Ready to architect your AI’s future? Robust, modular design keeps you agile as needs change.
Overcoming Challenges in Agentic AI Implementation
Implementing agentic AI presents multiple challenges that can undermine enterprise adoption if not addressed with careful planning and strategy. However, each core roadblock has practical solutions adopted by successful organizations.
Integration Complexity- Unifying legacy infrastructure with new cloud-based systems is a major hurdle. Smooth integration demands robust APIs, adaptable orchestration layers, and investment in foundational infrastructure before piloting AI at scale. Prioritizing agent-ready platforms and modular designs simplifies the integration process and improves long-term agility.
Data Silos - Fragmented, inconsistent, or low-quality data across departments leads to unreliable agentic AI decisions. Overcoming this requires establishing strong enterprise data governance, integrating data lakes or knowledge graphs, and using regular data audits and ML-driven data cleaning to unify and validate all data sources for actionable insights.
Security and Compliance- Agentic AI expands the risk landscape due to autonomous actions. Key controls include implementing zero-trust architecture, granular role-based permissions, privacy-preserving AI techniques (such as federated learning), clear logging of agent actions, and robust policy-driven oversight frameworks to comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Continuous Learning without Catastrophic Forgetting - Blending new real-time learning with established models can lead to “catastrophic forgetting,” where older knowledge is lost. Addressing this requires thoughtfully designed lifecycle management, combining continual retraining, historical data retention, and explicit memory modules to ensure agents learn incrementally while preserving core competencies.
ROI & Expectation Management: Unrealistic expectations for instant ROI or project simplicity cause disappointment; organizations need disciplined, “thin-slice” pilots that demonstrate value early and iteratively.
Effective agentic AI deployments use smart design, rigorous planning, incremental rollouts, and trusted SaaS partners to transform these complexities into manageable, strategic opportunities.
Future Trends in Agentic AI
The future of agentic AI is marked by transformative trends that will reshape enterprise operations, workforce dynamics, and autonomous decision-making. These trends reflect growing sophistication, expanded collaboration, and deeper industry integration.
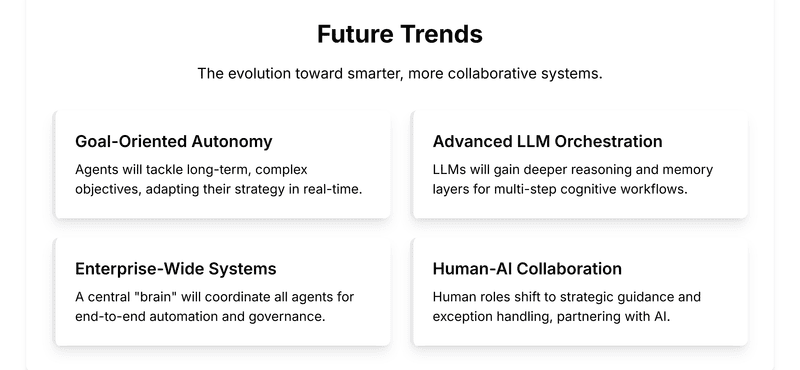
Real-Time, Goal-Oriented Autonomy
Agentic AI agents are evolving to execute complex, multi-step tasks by continuously learning and adapting to real-time data. These systems will not just automate routine processes but tackle long-term objectives, adjusting strategies on the fly as business and environmental contexts shift.
Expanding Agentic LLMs
Large language models are being paired with advanced reasoning, memory, and planning layers, resulting in agents capable of multi-step cognitive work. These hybrid LLM agents are moving beyond conversation, orchestrating workflows, analysing scenarios, and even acting autonomously across enterprise functions.
Enterprise-Wide Agentic AI Systems
Centralized agentic “brains” are increasingly deployed across organizations, coordinating dispersed agents through single orchestration frameworks like Zigment. This allows end-to-end automation, seamless integration of disparate data sources, and governance of agentic behavior at scale.
Smarter Human-AI Collaboration
As agentic AI automates more processes, human roles will shift from micro-management to strategic guidance, creativity, exception handling, and oversight. The future workforce will see humans and agents working as partners, each focusing on tasks aligned with their strengths AI for speed and volume, humans for nuance and judgment.
The Role of Zigment in an Agentic AI-Driven Architecture
While most platforms automate steps, Zigment unifies every customer signal into a single conversation-first memory layer, giving agents the context they need to act with autonomy.
Its Conversation Graph blends structured CRM data with unstructured human cues intent, mood, hesitation, urgency creating the real-time awareness that agentic systems depend on. From there, Zigment’s orchestration engine turns every signal into an adaptive next step, automating journeys not through rigid rules, but through understanding.
Zigment transforms fragmented workflows into a coordinated, goal-driven system exactly what Agentic Architecture was designed to enable.