Optimizing Retention: How Conversation Analysis Detects Churn Risk in the Lifecycle

Most churn doesn’t start with a decision.
It starts with a conversation.
A customer asks for clarification that feels unnecessary. A support chat stretches longer than it should. An email closes with, “We’re still evaluating.” None of these trigger an alert. Yet they’re often the earliest signs that confidence is slipping.
Optimizing Retention focuses on these real customer moments, signals embedded in chats, emails, and support conversations where hesitation, frustration, and doubt quietly surface. This is where retention teams gain an advantage.
We’ve learned that when you capture and analyze these qualitative signals, retention stops being reactive. Language patterns, emotional shifts, and expressed intent become measurable inputs that reveal churn risk well before usage drops or contracts come up for renewal.
In this article, we’ll show how conversation analysis turns everyday customer interactions into actionable insight, so you can intervene early, respond with precision, and retain customers when it still matters.
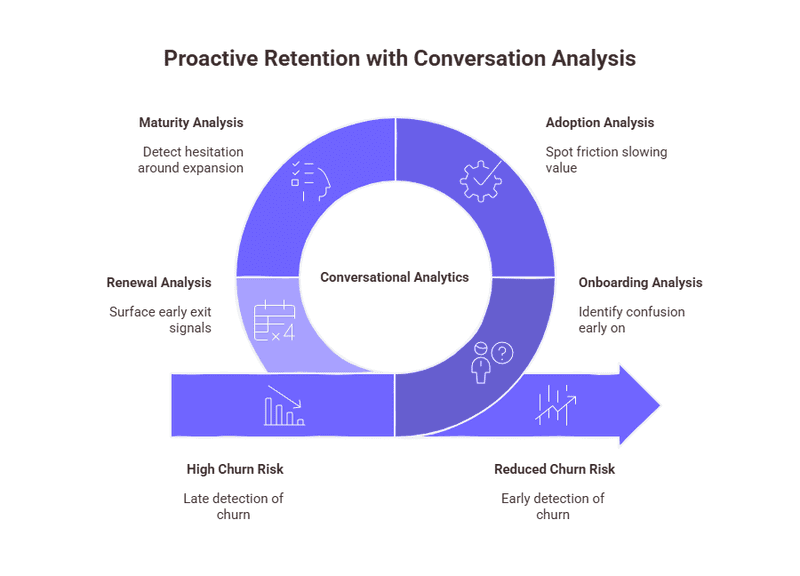
Optimizing Retention Through Conversation Analysis Across the Customer Lifecycle
Retention risk doesn’t appear at a single moment. It builds gradually as customers move through onboarding, adoption, expansion, and renewal. What changes across these stages is how that risk shows up.
Early in the lifecycle, customers ask exploratory questions. Later, their language becomes more precise and more revealing. A request for “best practices” can signal uncertainty. Repeated clarification questions often point to friction. Silence after a support interaction can be as meaningful as a complaint.
Conversation analysis helps teams capture these shifts in real time. By applying conversational analytics across chats, emails, and support threads, we can track how intent and confidence evolve as customers progress through the lifecycle.
This approach changes how retention works:
Onboarding: Identify confusion before it turns into disengagement
Adoption: Spot friction that slows value realization
Maturity: Detect hesitation around expansion or long-term fit
Renewal: Surface early exit signals months before contracts are discussed
Powered by conversational AI, these insights scale across thousands of interactions without relying on manual tagging or post-hoc analysis. The result is a clearer, earlier view of churn risk built from what customers actually say, not just what they do.
The Problem with Traditional Churn Models
Most churn models rely on what’s easy to measure. Product usage drops. Login frequency declines. Support tickets spike. These signals matter, but they arrive late.
By the time a customer’s behavior changes, the decision-making process is often already underway. Confidence has eroded. Alternatives have been considered. Internal alignment has shifted. None of this shows up cleanly in quantitative data.
Traditional churn models also struggle with context. A dip in usage could mean a seasonal slowdown. A surge in support tickets might reflect growth, not dissatisfaction. Without understanding the language behind these actions, teams are left guessing.
Here’s where the gap becomes clear:
Behavioral data shows what happened
Conversation data explains why it happened
When retention strategies rely only on dashboards, they miss the nuance that drives churn in later lifecycle stages. Conversations fill that gap by exposing intent, emotion, and unresolved friction, signals that appear long before a customer pulls away.
From Voice of Customer Research to Real-Time Retention Signals
For years, voice of customer research lived at the edge of decision-making. Surveys, interviews, and feedback forms produced valuable insights, but they arrived late and stayed isolated from day-to-day operations.
Conversations change that dynamic. Every chat, email, and support interaction carries context, what the customer needs, what’s blocking them, and how they feel about the experience in that moment.
When conversation analysis is applied at scale, these interactions become live retention signals. Teams can track:
Repeated topics that indicate unresolved friction
Shifts in language that suggest declining confidence
Emerging concerns tied to pricing, value, or fit
The difference is timing. Instead of reviewing feedback after churn occurs, retention teams gain visibility while customers are still engaged. Qualitative signals move from research artifacts to operational inputs, shaping how and when teams intervene across the lifecycle.
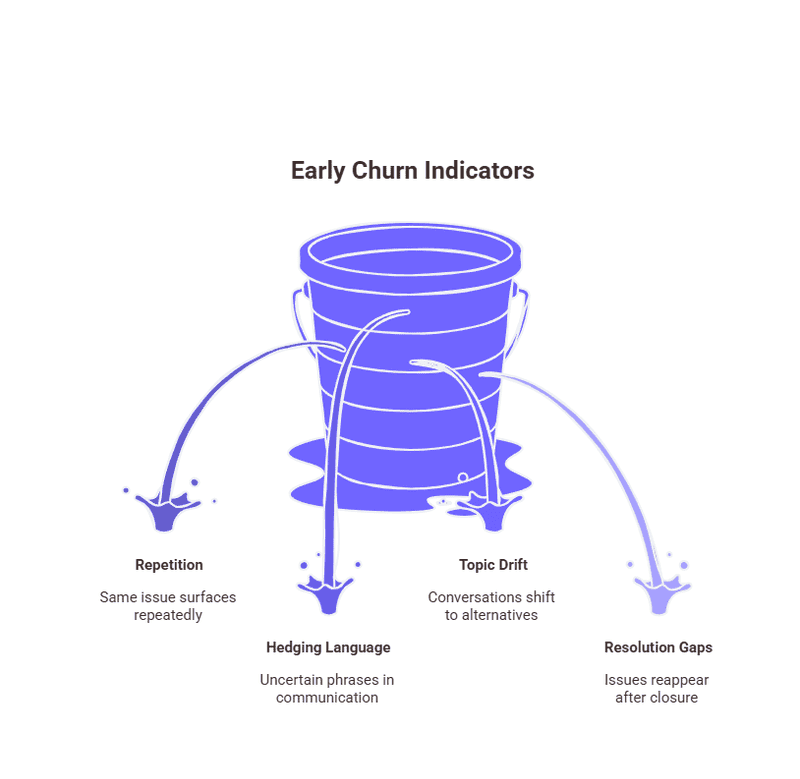
How Conversational Analytics Detects Churn Risk Early
Churn risk rarely appears as a single statement. It shows up as a pattern. Conversational analytics excels at spotting these patterns long before customers disengage.
Across thousands of interactions, certain signals repeat. Customers begin asking narrower questions. They revisit the same concerns across multiple conversations. Their language shifts from curiosity to evaluation.
Common early churn indicators include:
Repetition: The same question or issue surfaces across chats or emails
Hedging language: Phrases like “for now,” “just checking,” or “internally discussing”
Topic drift: Conversations move from usage to pricing, contracts, or alternatives
Resolution gaps: Issues marked as closed, yet referenced again later
Because these signals come directly from customer language, they surface earlier than usage drops or engagement declines. Conversational analytics turns everyday interactions into a continuous risk signal, one that updates as conversations evolve across the lifecycle.
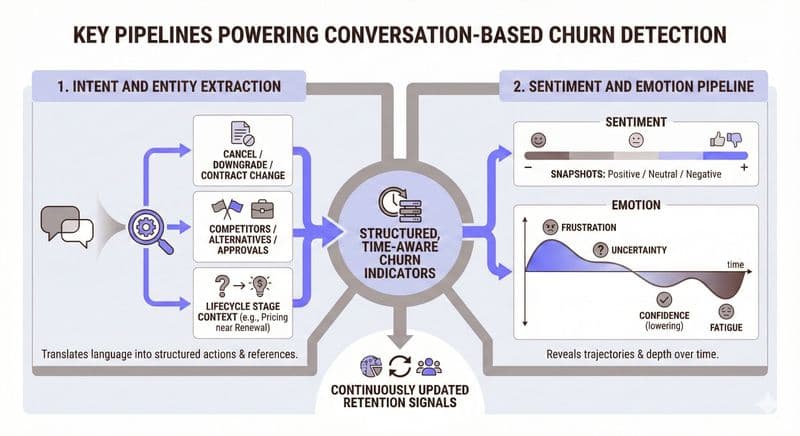
Key Pipelines Powering Conversation-Based Churn Detection
Conversation analysis works because it translates human language into structured signals that retention teams can act on. Two pipelines do most of the heavy lifting.
Intent And Entity Extraction
Customers often signal churn risk without saying it outright. Intent and entity extraction surfaces these moments by identifying what a customer is trying to do and what they’re referring to.
This includes detecting:
Language tied to cancellation, downgrade, or contract changes
Mentions of competitors, alternatives, or internal approvals
Questions that shift from “how do I use this?” to “do we still need this?”
When intent is mapped to lifecycle stage, these signals become highly predictive. A pricing question during onboarding means something very different from the same question near renewal.
Sentiment And Emotion Pipeline
Sentiment alone isn’t enough. Emotion provides depth.
By tracking frustration, uncertainty, confidence, and fatigue over time, emotion analysis reveals trajectories rather than snapshots. A neutral tone that slowly trends negative often signals risk earlier than an outright complaint.
Together, these pipelines turn conversations into structured, time-aware churn indicators, updated continuously as customers engage.
Turning Qualitative Signals Into Actionable Retention Triggers
Insights only matter when they drive action. Conversation analysis becomes powerful once qualitative signals are converted into clear retention triggers.
This happens by structuring conversational data into measurable inputs that update continuously. Instead of relying on a single score, teams can evaluate churn risk based on multiple dimensions.
Examples of actionable triggers include:
Rising frustration across consecutive support conversations
Repeated references to pricing, contracts, or internal justification
Declining confidence following unresolved issues
Explicit intent signals tied to downgrade or cancellation language
Each signal gains meaning when combined with lifecycle context. A single frustrated message may not require intervention. A pattern of frustration late in adoption often does.
When these triggers fire in real time, retention teams can respond with precision, adjusting outreach, escalating support, or changing the customer experience before disengagement sets in.
Why Later Lifecycle Stages Benefit Most From Conversation Analysis
As customers move deeper into the lifecycle, churn risk becomes harder to detect. Usage often stabilizes. Engagement appears healthy. The usual warning signs stay quiet.
Conversations tell a different story.
In later stages, customers use conversations to validate fit, justify spend, and manage internal expectations. Subtle shifts in language carry more weight. A question about alternatives. A request for export options. A sudden drop in responsiveness after support interactions.
Conversation analysis surfaces these signals when behavioral data stays flat. It helps teams catch risk while there’s still time to respond, before renewal discussions begin or decisions harden.
This is where qualitative data delivers its highest value: revealing exit signals hidden inside otherwise stable accounts.
Operationalizing Retention With Conversational AI
Capturing insights is only half the work. Retention improves when insights move fast.
Conversational AI enables teams to ingest and analyze conversations as they happen, across chat, email, and support channels, without manual review. Signals update continuously, reflecting the latest customer interactions rather than static snapshots.
This allows retention teams to:
Detect churn risk in real time
Prioritize accounts based on conversational signals
Respond while customers are still engaged
When conversation analysis operates live, retention shifts from retrospective analysis to proactive intervention. Teams stop reacting to churn. They start preventing it.
Conclusion: How Zigment Prevents Churn at the Moment It Forms
Retention improves when teams stop guessing and start listening. Conversations reveal intent, emotion, and confidence shifts long before churn shows up in metrics. When these signals are captured and acted on early, retention becomes a controlled outcome rather than a lagging result.
Zigment integrates conversation analysis directly into the orchestration layer. As customer interactions unfold, Zigment detects signals like frustration, hesitation, or intent to cancel in real time. These insights don’t sit in dashboards. They trigger an Instant Next Best Action, whether that means escalating support, adjusting outreach, or engaging the right team at the right moment.
This approach turns qualitative data into coordinated action across the lifecycle. Instead of reacting after customers disengage, teams intervene while trust can still be rebuilt.
When conversations guide orchestration, retention stops being reactive. It becomes intentional, timely, and far more effective.